Quantum Physics
Negative Wigner function at telecommunication wavelength
1 January 2017
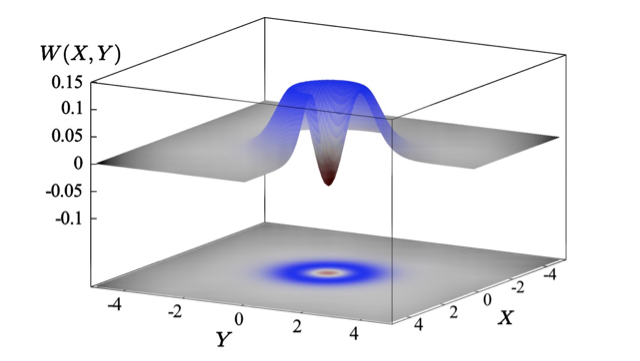
Photo: Ag Schnabel
The Wigner function is a quasi-probability density function that describes a quantum state. The word “quasi” refers to the fact that the Wigner function can have negative values, which is unphysical for a probability density function. Number states (Fock states) as well as cat states are examples having (partly) negative Wigner functions. These states are important resources in quantum information. Our work, for the first time, produced, and directly measured with balanced homodyne detection, a state of light at the telecommunication wavelength of 1550nm revealing a negative Wigner function.
Fig.: From our data reconstructed Wigner function of a single-photon-subtracted, weakly squeezed vacuum state. The data are not corrected for any kind of optical loss. Around the origin, a value reaches −0.063 ± 0.004. This value achieves about 20% of the strongest negativity possible of −1/π ≈ −0.318, which corresponds to a perfect measurement on a pure single-photon Fock state.
Christoph Baune, Jaromír Fiurášek, and Roman Schnabel, Phys. Rev. A 95, 061802(R) (2017).
