Technology Platform CHyN Clean Room Bahrenfeld
The technology platform CHyN clean room with focus on complex nanofabrication processes is a state-of-the-art clean room facility that’s designed as a clean room ISO-Class 4 standard – an ultra-clean, particle- and dust free user lab. Equipped with cutting-edge instrumentation, it provides an ideal environment for top-level interdisciplinary research.
The lab facility is jointly operated by three organizations – Universität Hamburg (UHH), Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron (DESY) and Max Planck Institute for the Structure and Dynamics of Matter (MPSD). The lab is located within the Center for Hybrid Nanostructures (CHyN) Building 600 on the research campus, Science City Hamburg Bahrenfeld (SCHB).
Organization
The CHyN clean room is operated and managed by a coordinator, engineers and senior researchers from all the three organizations – UHH, DESY and MPSD – supervised by the clean room board. The board oversees the scientific directions and strategic development of the clean room.
The clean room coordinator serves as the central communication interface between users, staff, facility management, and the management board. Additionally, the coordinator oversees day-to-day operations and ensures smooth and efficient usage processes.
Curious to know more about the CHyN clean room facility?
The CHyN clean room is structured into two main areas: the Yellow Room and the White Room, supported by associated user labs located outside the cleanroom complex. These labs enable advanced processing of extremely small structures down to 500 nanometers and below, high-resolution imaging, elemental analysis, and ion implantation.
The Yellow Room – Structuring at the Nanoscale
The Yellow Room is specifically designed for preparative synthesis processes such as wet-chemical processes and is also used for analytical work. It is particularly suited for lithographic structuring, conducted in a UV-protected environment. This allows for the fabrication of structures ranging from the sub-micrometer to the nanometer scale.
In addition to structuring, important material properties can be directly qualified in this area, including:
- surface roughness,
- thickness of deposited layers,
- and etch depth of structured materials.
The White Room – Deposition and Characterization of Functional Materials
Adjacent to the yellow room, the white room focuses on the nano-deposition of various thin film systems including:
- semi-conductor materials,
- functional materials such as bismuth or hafnium,
- insulating oxide or nitride layers for passivation,
- and metallic materials like gold, titanium, platinum, aluminum, or copper etc.
Moreover, the white room enables dry etching for structural definition or patterning and optical characterization of deposited layers. These capabilities make it possible to design and transform materials into highly functional structures.
Access and Usage
Access and Usage of the CHyN clean room facility is a two-step process. After a short general safety introduction, process flow applications are submitted by respective research team and approved by the facility to ensure a safe and professional working environment. The facility is staffed with process instructors providing hands-on training and guiding the registered users on the proper operation of the complex equipment. Users can make independent bookings on the various equipment after completing the selected training sessions and subscription of the registered booking tool – cluster market – of the lab facility.
The dates and location for the monthly routine safety introduction could be downloaded here (click pdf file)
Contact
Should you require more information or interested in getting access to use the technology platform CHyN clean room, you could reach out to us through: rrbuch"AT"physnet.uni-hamburg.de.
Dr.-Ing. Lewis Olaniyi Akinsinde
Coordinator Clean Room Technology Platform
Office: CFEL - Center for Free Electron Laser Science Hamburg, Building 99, Room O1.125
Luruper Chaussee 149
D-22761 Hamburg
Tel.: +49 (0)151 5538 8158
E-Mail: lewis-olaniyi.akinsinde@uni-hamburg.de
Users
The users are mainly undergraduate students from the bachelor’s, and master’s to the PhD level, post-doctoral researchers, and senior scientists carrying out fundamental research in the fields of pharmacy, nanotechnology, biophysics, material science, microelectronics, life science, and quantum technology. Researchers from other disciplines are also welcome.
Available Equipment in the user lab facility
Currently, more than 20 high-precision instruments are available in the CHyN clean room facility. These can be combined into complex process chains - supported by experienced cleanroom staff - to carry out demanding research and development projects. Below is an overview of selected systems and technologies in the fields of lithography, coating, patterning, and analytical approach.
Lithographic Structuring Techniques
Electron Beam Lithography (EBL Raith Voyager)
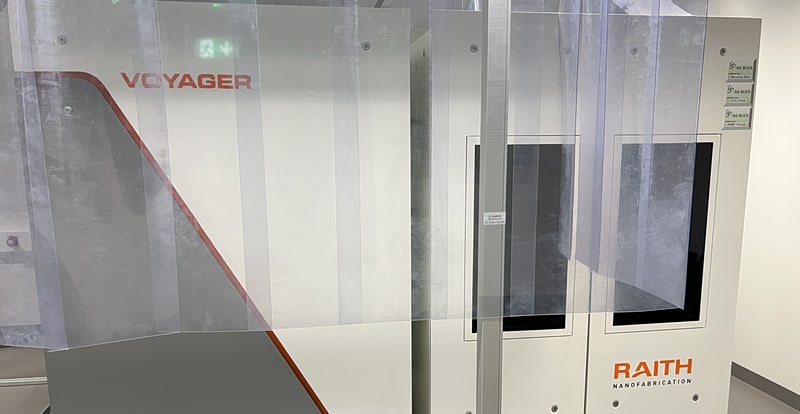

The Voyager system from Raith is a high-precision 50 kV electron beam lithography platform with a nominal accuracy of 2 nm and a minimum feature size of 6 nm (internally, we have successfully achieved 10 nm lines). It enables the exposure of substrates ranging from 5 mm to 4 inches. The Automatic Height Sensing system (update in 2024) ensures optimized focus adjustment across the entire wafer surface, minimizing focus errors and stitching artifacts.
The 2019 upgrades significantly enhance functionality: TRAXX (FBMS) enables the seamless patterning of centimeter-long paths, while PERIODIXX (MBMS) allows the fabrication of stitch-free periodic structures over large areas.
UV Lithography Mask aligner MJB4
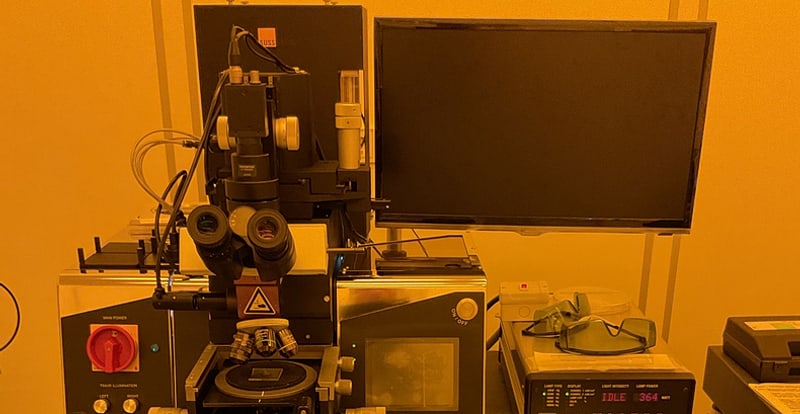

The UV lithographic structuring is possible on the Karl Süss MJB4 mask aligner system inside the yellow room. The MJB4 is equipped with a powerful 350W high pressure mercury lamp emitting ultraviolet (UV) light in the UVA (ca. 365 nm, i-line) and UVB (ca. 313 nm, h-line) ranges. The MJB4 supports contact and proximity exposure modes. The smallest achievable feature size depends on the exposure mode: Hard contact roughly 1-micron, soft contact / proximity around 2 – 5 microns (this varies based on the gap distance). The manual mask aligner supports wafers and substrates size up to 100 mm (4”) diameter with uniformity in the illumination/ exposure over a wide range are applicable. The XYZ table allows horizontal displacement, tilting and rotation of the stage with micrometer screws. The optical alignment is handled from the top side and the vacuum is used in fixing the sample on the stage. The system is widely used for research in microfluidics, MEMS, and other microfabrication applications requiring high alignment accuracy.
Raith Picomaster: a high-resolution Laser writer
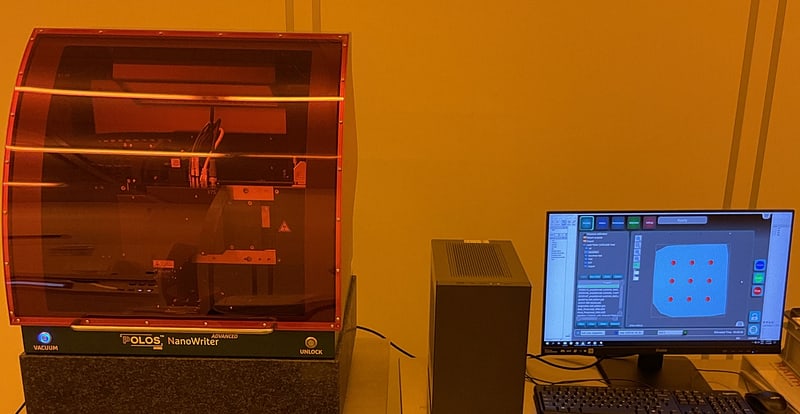

The Raith PICOMASTER comprises an advanced laser lithography system engineered for high precision, maskless lithography applications. It can accommodate a range of substrate sizes and is specifically designed for research and prototyping projects. With exceptional resolution capabilities and adjustable writing speeds, it establishes a benchmark in advanced lithography technology.
Key Technical Specification:
- Scan speed limits: maximum/ minimum scan speed of 200/20 mm/s for both directions with a movement range of 115 mm.
- Step size: minimum step size of 5 nm for the scan axis and 20 nm for the step axis respectively. The resolution can be as high as 2 nm in the ideal case.
- XY-motion limits: the substrate size can vary from 5 x 5 to 125 x 125 mm2, and it can accommodate various substrate types (sapphire, Silicon, etc.,). The exposable area is 110 x 110mm2.
Layer Deposition and Coating Method
Heimerle-Meule PGG 10 Electroplating Instrument
Heimerle-Meule PGG 10 is a user-friendly instrument used for galvanic deposition of an extensive selection of metals, including rhodium, gold, silver, palladium, and copper, except chrome deposition.
The instrument offers electrolyte heating, with 5 °C precision in 30-85 °C interval using a quartz glass immersion heater. It also has a sample motion option in two tanks to improve the plating uniformity. The electroplating system can be fed at the 0- 10 Volt/Ampere interval via stainless-steel anodes and cathodes and set with 0.2 mV/mA unit precision in this range.
The system has three tanks that help to handle three reactions at the same time. Chemically resistive and large tanks are suitable for various process requests, like with 4” wafers, as well as small samples. In case the small samples are used, the custom-made titanium sample holder could be introduced into the system easily. The instrument is mostly used for Cu electroplating in our cleanroom. Other possible deposition metals would be evaluated and integrated according to user demands in time.
Creamet 450 E-Beam S3 Coating System
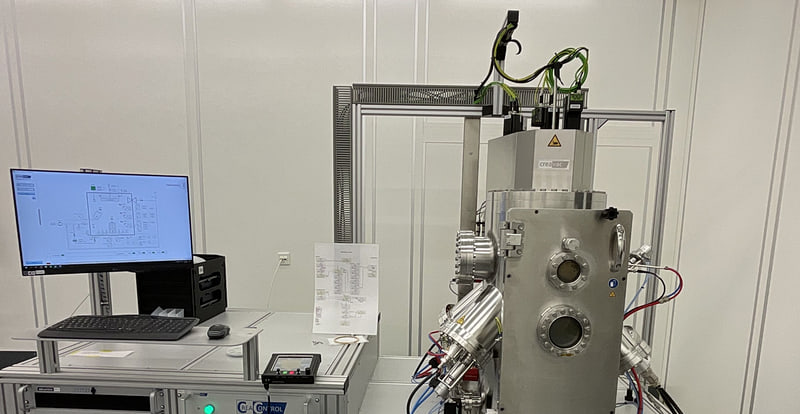
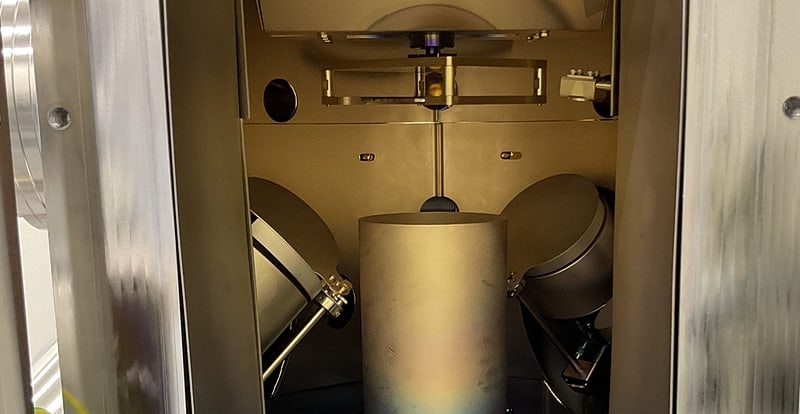


The CREAMET 450 e-beam S3 from CREAVAC is a high-vacuum coating system that operates with a multi-pocket electron beam evaporator (6 pockets) and achieves a base vacuum of < 5 X 10⁻⁷ mbar to enable precise thin-film deposition. Substrates up to 4 inches can be optimally aligned using a rotating and tilting holder, ensuring uniform coatings. Additionally, three magnetron sputter sources are available, which can operate with RF, DC, and HiPIMS technology to evaporate various materials like Gold, Titanium, Bismuth, Platin etc. Furthermore, an ion beam source allows for targeted sputtering and control of the layer morphology. The gas inlet system enables the precise control of process gases such as argon for sputtering processes or reactive gas-phase deposition. The CREACONTROL system provides precise process control with recipe management, real-time monitoring, and safety functions to ensure stable and reproducible coating conditions.
AT200M: a versatile tabletop Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) system

AT200M is the smallest footprint ALD (Atomic Layer Deposition) tool available on the market. It is well-fitted for tabletop operation, and the small chamber size also ensures a high level of vacuum and small interaction volume during the deposition process. The system is equipped with one precursor and one counter-reactant, and all parts (precursor, manifold, chamber) can be heated to ensure no condensation. The deposition Chamber is fitted for one 2” wafer. Three precursors are possible now, including Platinum (Pt), Hafnium (Hf), Titanium (Ti), and Silicon (Si). In the future, Aluminium (Al) precursor could be added. Three actants are available: H2O, O2, and O3, with the help of an Ozone generator. This allows the deposition of Si/SiO2, Hf/HfO2, Ti/TiO2, Pt, and Al/Al2O3 soon. The precursor and gas manifold can be heated up to 150°C, and the stainless-steel chamber itself can be heated up to 300°C. A moderate vacuum condition is possible via constant and continuous pumping of the chamber during the procedure with a flow of nitrogen gas. The minimum pressure is below 20 mbar is achievable with the AT200M. The typical deposition time for depositing for example standard recipe of 10nm Ti layer will take roughly 20 minutes.
Plasma Enhanced CVD Systems SI 500D 214
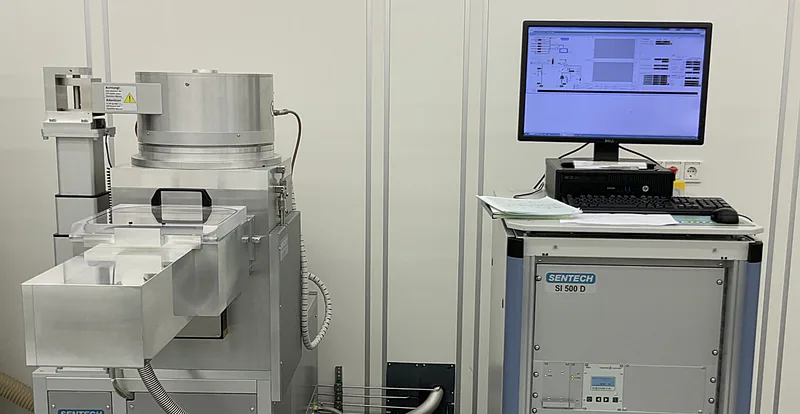
The inductively coupled plasma enhanced CVD (PECVD) system SI 500D 214 from Sentech is designed for high density, low ion energy, and low-pressure plasma deposition of dielectric films and low-damage, very low temperature deposition of passivation layers like nitrides. The attractiveness of low etch rate, high breakdown voltage, low stress, no damage of substrate facilitates an outstanding property of the deposited layers of thin film.
The Key Features and benefits include
PTSA (Planar Triple Spiral Antenna) plasma source
- generates homogeneous and uniform plasma
- high ion density (in Ar plasma)
- low ion energy distribution promotes high-quality and low-damage deposition of oxides and nitrides (SiOx, SixNy, SiC, and doped layers.
dynamic temperature-controlled substrate electrode for high-quality layer deposition
- Helium back side cooling and substrate back side temperature sensing
reproducible processe
- fully controlled vacuum system,
- different levels of automation ranging from load-lock loading to the process chamber
- Process gases: NH3, SiH4 in He, CF4, O2 and Ar
Patterning, Implantation and Etching Techniques
FIB-SEM - ZEISS Crossbeam 550
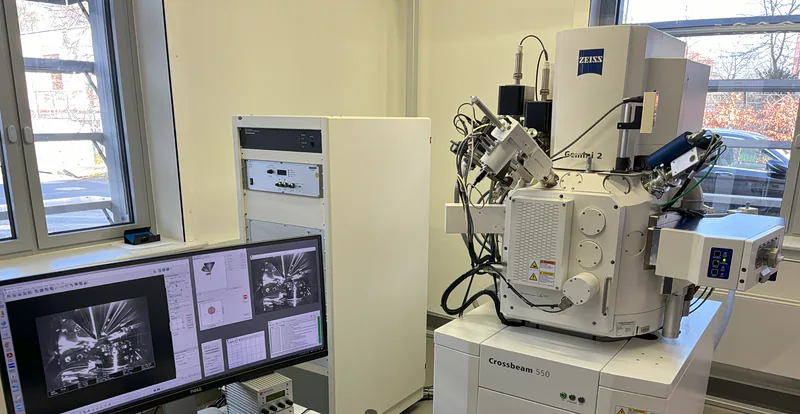

The FIB-SEM (ZEISS Crossbeam 550, is a useful tool to investigate specimens by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in combination with optional focused ion beam (FIB) milling. Furthermore, elemental analysis of the specimen material can be conducted by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The integrated airlock chamber ensures fast sample exchange and short pumping times, accelerating the throughput for the analysis of samples in the high-vacuum environment of the FIB-SEM main chamber.
The SEM part is equipped with the Gemini 2 column, which allows for high-resolution imaging (resolution below 10 nm) of all kinds of conductive and non-conductive materials facilitated by the adjustable acceleration voltage and electron beam current settings. Various micro- and nanostructured samples are imaged with the FIB-SEM, such as nanofluidic devices based on silicon or polymer substrates, porous silicon oxide, zinc oxide nanowires on free-standing nanomembranes, and carbon nanotubes on 3D-printed substrates. Moreover, distortion-free images of large sample areas and tilted specimens are generated by combining high image store resolutions (up to 32k x 24k pixels) with the depth of field mode. Thereby, impressive overview scans can be produced, for example, to analyze the homogeneity of silicon nanowire arrays, which were fabricated by a sequence of electron beam lithography (EBL) and reactive ion etching (RIE), or to view the distribution of neurons cultured on designed nanowire arrays.
The ion beam currents for the FIB milling using a gallium reservoir can be selected from a wide range (1 pA - 100 nA). Lower ion beam currents are ideal to precisely cut through nanometer-sized, hollow Cu2O cubes, or to produce a cross section of a tube that connects scaffolds for neuron culturing to observe both, its homogenous Al2O3 coating generated by atomic layer deposition (ALD) and the axon grown through this tube. Higher ion beam currents are selected to accelerate material removal over larger sample areas. This technique was used for generating cross sections through cellular structures situated on nanowire arrays for inspecting the contact region between the nanowire tips and the cell membrane.
The sample analysis is further enhanced by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) for element identification. This part of the instrument is used to study the elemental composition and purity of thin films and nanostructures, such as superconducting niobium titanium nitride thin films deposited by plasma-enhanced ALD and ZnO nano whiskers grown by metal organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD).
Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) System SI 500 215 for Reactive Ion Etching (RIE)
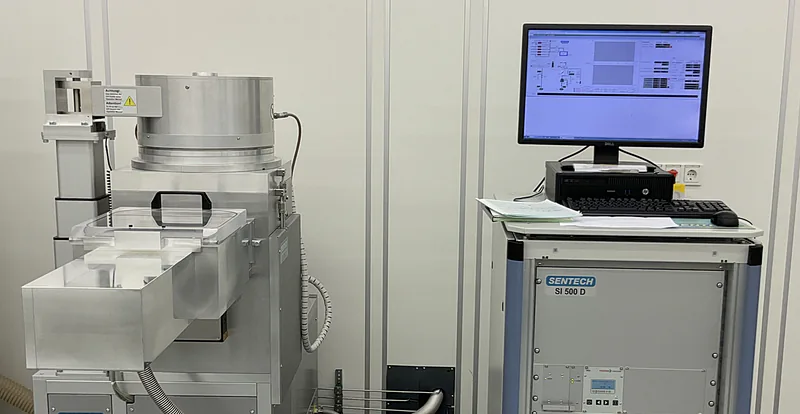

The SI 500 ICP-RIE from the company Sentech is a high-end plasma etch system that uses an inductively coupled plasma source with low ion energy for low-damage etch and nano structuring.
The system features and properties include:
PTSA (Planar Triple Spiral Antenna) plasma source
- generates homogeneous plasma
- high ion density (in Ar plasma)
- low ion energy distribution less sample damage during etching at low pressures
dynamic temperature-controlled substrate electrode
- Helium back side cooling and substrate back side temperature sensing
- over wide temperature range 0°C – 250°C
reproducible processes
- fully controlled vacuum system,
- different levels of automation ranging from load-lock loading to the process chamber
- Process gases: SF6, CHF3, C4F8, O2 and Ar.
List of Equipment
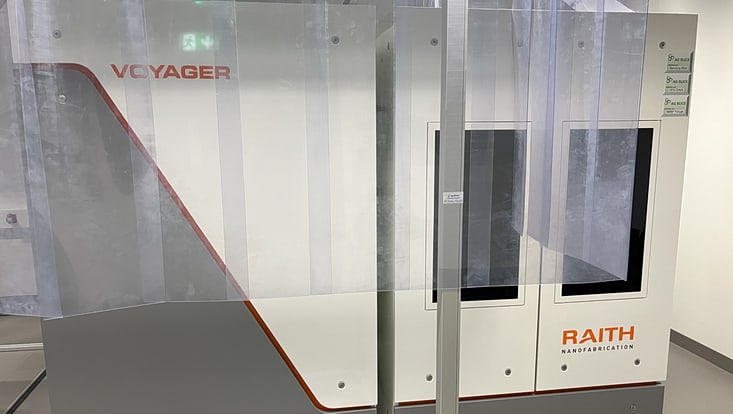

Photo: UHH/Akinsinde
Raith Voyager E-Beam Lithography System
Field of Application: The high-precision 50 kV electron beam lithography platform is for lithographic structuring purposes. The Voyager system has a nominal accuracy of 2 nm and a minimum feature size of 6 nm. The exposure of substrates sizes ranging from 5 mm to 4'' diameter is possible. Its recent software update automatic height sensing system allows optimized focus adjustment across the entire wafer surface, minimizing focus errors and stitching artifacts.
Location: EBL Voyager lab, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 063
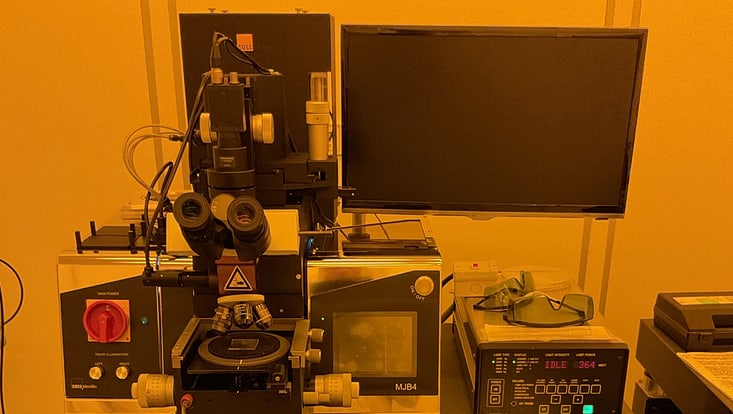
Photo: UHH/Stützle
UV Lithography Mask Aligner MJB4 from Karl Süss company
Field of Application: The MJB4 model Mask aligner is typically applied as a UV lithographic structuring. With it's equipped powerful 350W high pressure mercury lamp, the emission of two characteristics ultra-violett wavelength spectrum 365 nm and 313 nm useful for micro patterning are obtainable. Contacts and proximity exposure modes are possible. The smallest achievable feature size depends on the exposure mode: Hard contact roughly 1-micron, soft contact / proximity around 2 – 5 microns. Wafers and substrates size up to 100 mm (4”) diameter with uniformity in the exposure over a wide range are applicable.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 034
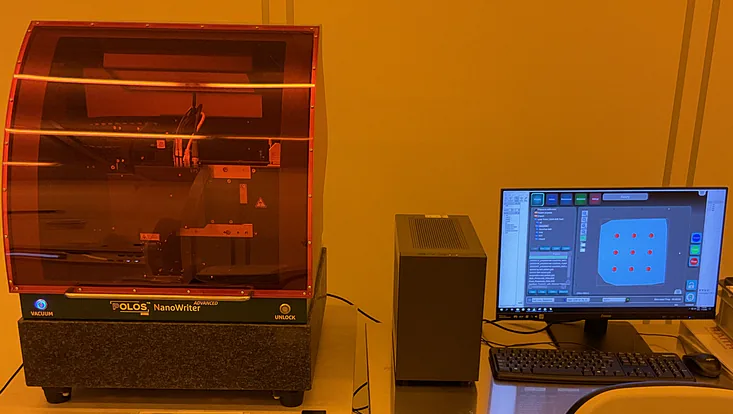

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Raith Picomaster: a high-resolution Maskless Laser Writing System
Field of Application: The PICOMASTER from Raith comprises an advanced laser lithography system engineered for high precision, maskless lithography applications.
Key Technical Specification:
- Scan speed limits: maximum/ minimum scan speed of 200/20 mm/s for both directions with a wide movement range of 115 mm.
- Step size: minimum step size of 5 nm for the scan axis and 20 nm for the step axis respectively. An optimal resolution as high as 2 nm is achievable.
- XY-motion limits: the substrate size can vary from 5 x 5 to 125 x 125 mm2, and various substrate types (sapphire, Silicon, etc.,). The exposable area is 110 x 110mm2.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 034
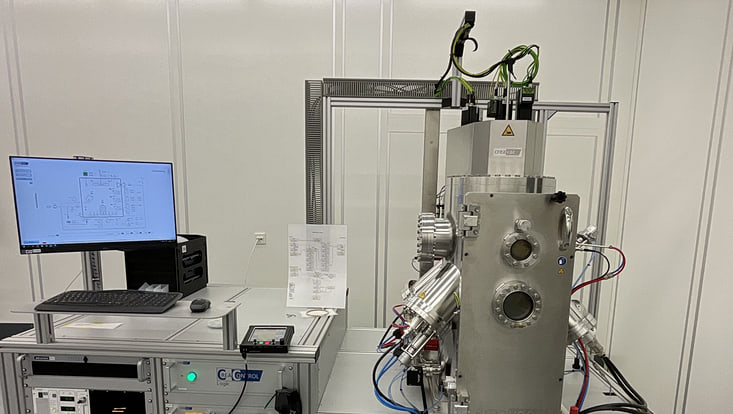
Photo: UHH/Stützle
High-vacuum Coating System from Creavac: Creamet 450 E-Beam S3 Coating System
Field of Apllication: The CREAMET 450 e-beam S3 from CREAVAC is a high-vacuum coating system that operates with a multi-pocket (6 pockets) electron beam evaporator and achieves a base vacuum of < 5 X 10⁻⁷ mbar to enable high quality hin-film deposition. Substrates up to 4'' can be optimally aligned using a rotating and tilting holder, ensuring uniform coatings. Additionally, three magnetron sputter sources are available, which can operate with RF, DC, and HiPIMS technology to evaporate various materials like Au, Ti, Pt etc. Furthermore, an ion beam source allows for targeted sputtering and control of the layer morphology.
Location: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
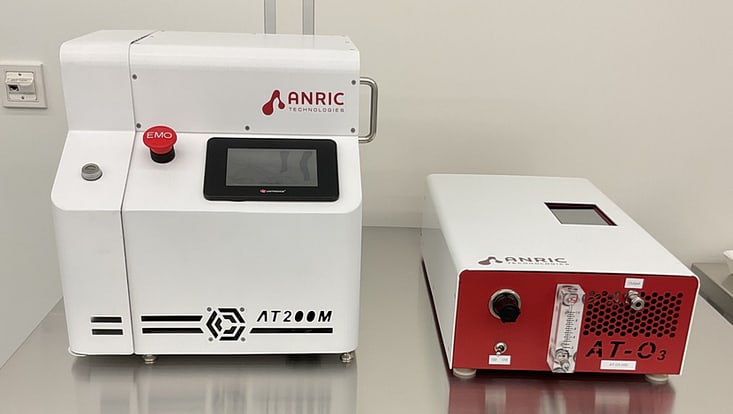

Photo: UHH/Stützle
AT200M Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) System
Field of Application: The ATM 200M is the smallest footprint ALD tool available on the market and is well-fitted for tabletop operation, and the small chamber size also ensures a high level of vacuum and small interaction volume during the deposition process. The system is equipped with one precursor and one counter-reactant, and all parts - precursor, manifold, chamber - can be heated to ensure no condensation. The deposition chamber is fitted for one 2” wafer and the deposition of thin film layers Si/SiO2, Hf/HfO2, Ti/TiO2, and Pt are possible. The typical deposition time for depositing e.g.standard recipe ca. 10nm Ti layer could last roughly 20 minutes.
Location: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
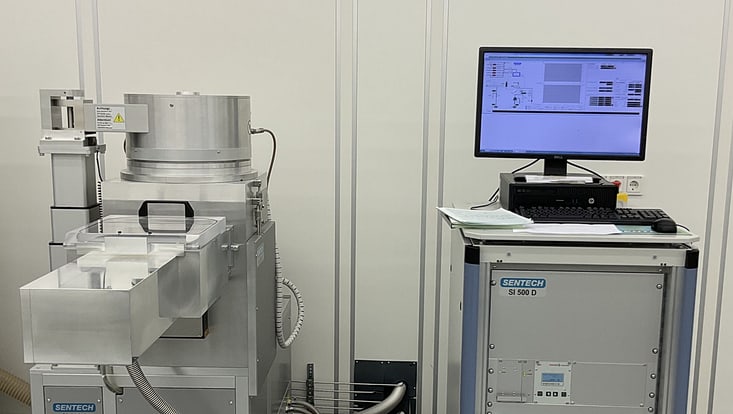

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Plasma Enhanced CVD Systems SI 500D 214 from Sentech
Field of Application: The inductively coupled plasma enhanced CVD (PECVD) system SI 500D 214 from Sentech is designed for high density, low ion energy, and low-pressure plasma deposition of dielectric thin films and low-damage, very low temperature deposition of passivation layers like nitrides. The attractiveness of low etch rate, high breakdown voltage, low stress, no damage of substrate facilitates an outstanding property of the deposited layers of thin film.
The key features and benefits of the PECVD system include reproducible processes that's achievable via fully controlled via systems and process gases are NH3, SiH4 in He, CF4, O2 and Ar.
Location: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
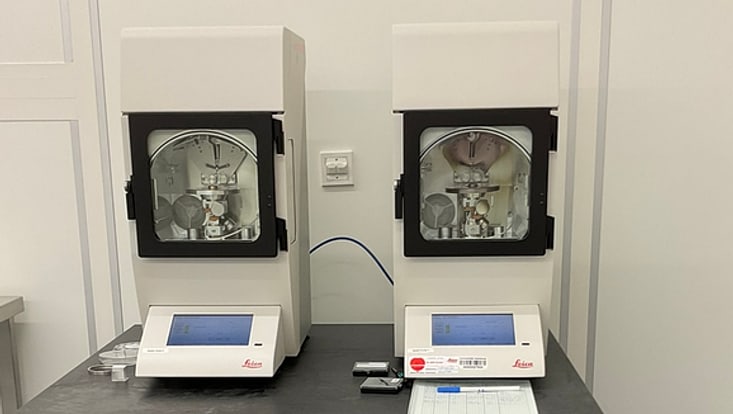

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Leica EM ACE600 - TDS 02-2022 Sputter Coater
Field of Applications: The Leica ACE600 sputter coater xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
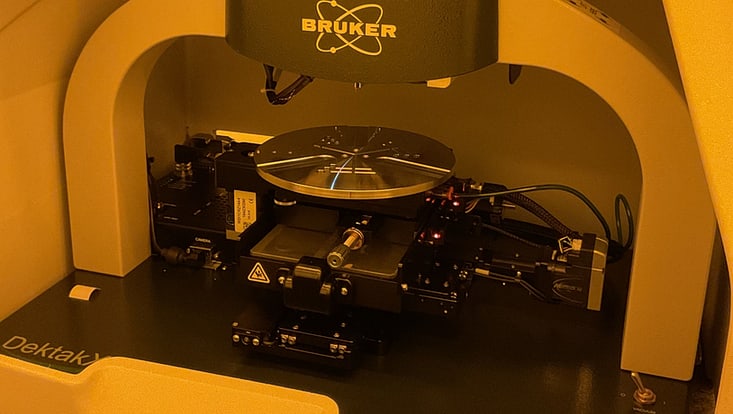
Photo: UHH/Stützle
DEKTAK
Field of Application: XXXXXXXXXX.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 034
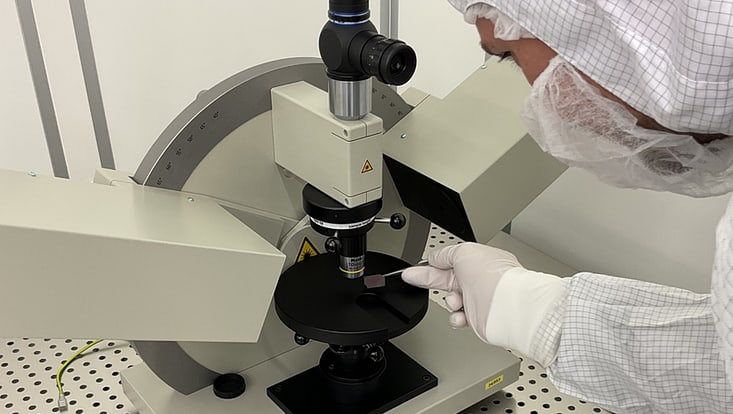

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Ellipsometer
Field of Applications: The Leica ACE600 sputter coater xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
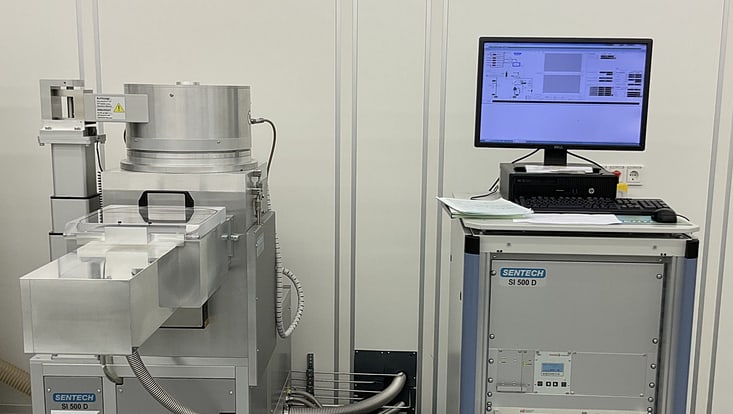

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Reactive Ion Etcher SI 500 215
Field of Applications: The SI 500 ICP-RIE from the company Sentech is a high-end plasma etch system that uses an inductively coupled plasma source with low ion energy for low-damage dry etch and nano structuring of different substrates mostly wafers, sapphire and glass. The system has its unique feature in processes reproducibility achievable through the integrated full controlled vacuum system, different levels of automation ranging from load-lock loading to the process chamber. The following standard reactive process gases SF6, CHF3, C4F8, O2 and Ar are utilized for the dry etching process.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035
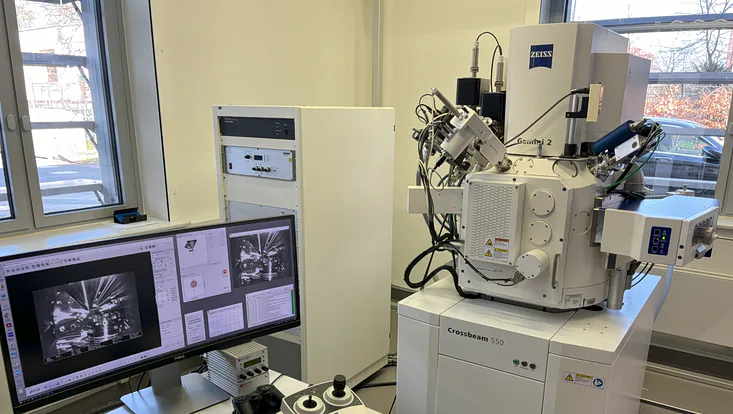

Photo: UHH/Akinsinde
FIB-SEM - ZEISS Crossbeam 550 coupled FIB
Field of Application: The FIB-SEM (ZEISS Crossbeam 550, is used in investigating the structure and morphology - high-resolution imaging with resolution below 10 nm of all kinds of conductive and non-conductive materials is possible - of different specimens by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) in combination with optional focused ion beam (FIB) milling for patterning purpose. Also, elemental analysis of the specimen material can be conducted by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS). The sample analysis enhanced by EDS to study the elemental composition and purity of thin films, micro- and -nanostructures.
Location: SEM-FIB lab, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 060
List of Equipment

Photo: UHH/Akinsinde
Raith Voyager Elektronenstrahl Lithografie
Anwendungsbereiche: Die Elektronenstrahllithografie mit dem Raith Voyager-System ermöglicht durch ihre hohe Präzision die Herstellung feinster Strukturen bis in den Nanometerbereich. Mit einer Spannung von 50 kV, einer nominellen Genauigkeit von 2 nm und einer realisierbaren Strukturbreite bis hinunter zu 10 nm eignet sich dieses System ideal für komplexe Lithografiemuster. Dank automatisierter Höhensensorik und Funktionen wie TRAXX und PERIODIXX lassen sich strukturierte Pfade und periodische Muster über große Flächen stitch-frei realisieren.
Standort: EBL Voyager Labor, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 063, SCHB

Photo: UHH/Stützle
UV Lithografie Mask Aligner MJB4
Anwendungsbereiche: Im Bereich der UV-Lithografie kommt der Mask Aligner Karl Süss MJB4 zum Einsatz. Dieses System eignet sich besonders für mikrofluidische Anwendungen, MEMS und weitere mikrostrukturierte Designs. Mit Belichtungsmodi wie Kontakt und Proximity lassen sich Strukturen ab etwa 1 µm realisieren, wobei eine hochpräzise Ausrichtung durch einen XYZ-Tisch gewährleistet ist.
Standort: CHyN Reinraum, Gelblichtraum, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 034,SCHB

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Raith Picomaster: Hochauflösender Maskenloser Laserschreiber
Anwendungsbereiche: Der Raith PICOMASTER ist leistungsfähiger maskenloser Laserwriter für die hochpräzise Belichtung verschiedenster Substrattypen. Mit einer Schreibauflösung von bis zu 2 nm auf versdchiedene Substraten wie SiO2 Wafer, Glas usw. und einer flexiblen Substratgröße bis 125 mm² bietet er herausragende Möglichkeiten für Forschung und Prototyping.
Standort: CHyN Reinraum, Gelblichtraum, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 034, SCHB

Photo: UHH/Stützle
DEKTAK
Field of Application: XXXXXXXXXX.
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 034

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Hochvakuum Beschichtungsanlage: Creamet 450 Elektronenstrahl S3 Beschichtungssystem
Anwendungsbereiche: Für hochpräzise Beschichtungsprozesse steht die CREAMET 450 E-Strahl S3 von CREAVAC zur Verfügung. Dieses Hochvakuum-System ermöglicht sowohl die Elektronenstrahlverdampfung als auch das Sputtern verschiedenster Materialien – unterstützt durch moderne Technologien wie RF-, DC- und HiPIMS-Verfahren. Die integrierte Ionenstrahlquelle erlaubt eine gezielte Beeinflussung der Schichtmorphologie, während die intelligente CREACONTROL-Steuerung eine stabile, reproduzierbare Prozessführung sicherstellt.
Standort: CHyN Reinraum, weiße Raum, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 035,SCHB

Photo: UHH/Stützle
AT200M Atomen Lagenabcheidung (ALD) System
Anwendungsbereiche: ein kompaktes ALD-Gerät (Atomlagenabscheidung), das für die hochpräzise Abscheidung ultradünner Schichten auf 2-Zoll-Wafern konzipiert ist. Mit beheizbaren Komponenten und einer Auswahl an bis zu drei Präkursoren (z. B. Pt, Ti, Hf, Si) sowie Reaktionsmitteln wie H₂O, O₂ und O₃ eignet sich das System für die Herstellung funktionaler Schichten wie Al₂O₃, TiO₂ oder SiO₂ mit höchster Homogenität.
Standort: CHyN Reinraum, weiße Raum, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 035, SCHB

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Induzierte Plasma CVD Systeme SI 500D 214
Anwendunsgereiche: Für die Abscheidung von Passivierungsschichten kommt das PECVD-System SI 500D 214 von Sentech zum Einsatz. Die plasmaunterstützte chemische Gasphasenabscheidung erlaubt die Herstellung dichter, spannungsarmer dielektrischer dünnen Schichten bei niedrigen Temperaturen.
Standort: CHyN Clean room, White room, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 035,SCHB

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Leica EM ACE600 - TDS 02-2022 Sputter Coater
Field of Applications: The Leica ACE600 sputter coater xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Ellipsometer
Field of Applications: The Leica ACE600 sputter coater xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Location: CHyN Clean room, Yellow room, CHyN Bldg. 600, RM EG. 035

Photo: UHH/Stützle
Reaktive Ionen Ätzen SI 500 215
Anwendungsbereiche: Für das reaktive Ionentiefätzen (RIE) kommt das SI 500 ICP-RIE-System von Sentech zum Einsatz. Mit seiner induktiv gekoppelten Plasmaquelle, der Planar Triple Spiral Antenna (PTSA), erzeugt es ein homogenes Plasma mit hoher Ionendichte bei niedriger Energie – ideal für schonendes, präzises Strukturieren. Die temperaturgeregelte Substratelektrode sowie das automatisierte Vakuum- und Gassystem ermöglichen reproduzierbare Prozesse bei höchster Kontrolle.
Standort: CHyN Reinraum, Gelblichtraum, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 035,SCHB

Photo: UHH/Akinsinde
FIB-SEM - ZEISS Crossbeam 550 gekoppelte Fokussierte Ionenstrahl (FIB)
Anwendungsbereiche: Zur hochauflösenden Strukturierung und Analyse steht das ZEISS Crossbeam 550 zur Verfügung – ein kombiniertes FIB-SEM-System (Focussed Ion Beam / Scanning Electron Microscope). Dieses Instrument ermöglicht neben der Bildgebung im Sub-10-nm-Bereich auch gezielte Materialabtragungen und Querschnittanalysen mithilfe eines Gallium-Ionenstrahls. Ergänzt wird das System durch ein EDS-Modul zur Elementanalyse. Es eignet sich besonders zur Untersuchung mikro- und nanostrukturierter Proben sowie zur Charakterisierung funktionaler Dünnschichten und komplexer Zell-Nanostruktur-Interaktionen
Standort: FIB Labor, CHyN Geb. 600, RM EG. 060, SCHB
Publications
2024
- Haugg, S.; Mochalski, L. F.; Hedrich, C.; González Díaz-Palacio, I.; Deneke, K.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R. H. Field Emission from Carbon Nanotubes on Titanium Nitride-Coated Planar and 3D-Printed Substrates. Nanomaterials 2024, 14 (9), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano14090781.
2022
- Haugg, S.; Hedrich, C.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R. H. Field Emission Characteristics of ZnO Nanowires Grown by Catalyst-Assisted MOCVD on Free-Standing Inorganic Nanomembranes. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2022, 55 (25), 255104. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6463/ac5d05.
- Harberts, J.; Siegmund, M.; Hedrich, C.; Kim, W.; Fontcuberta i Morral, A.; Zierold, R.; Blick, R. H. Generation of Human IPSC-Derived Neurons on Nanowire Arrays Featuring Varying Lengths, Pitches, and Diameters. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9 (24), 2200806. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202200806.
- Grote, L.; Seyrich, M.; Döhrmann, R.; Harouna-Mayer, S. Y.; Mancini, F.; Kaziukenas, E.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I.; A. Zito, C.; Vasylieva, O.; Wittwer, F.; Odstrčzil, M.; Mogos, N.; Landmann, M.; Schroer, C. G.; Koziej, D. Imaging Cu2O Nanocube Hollowing in Solution by Quantitative in Situ X-Ray Ptychography. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13 (1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-32373-2.
- Esmek, F.M; Erichlandwehr, T; Brkovic, N; Pranzner, N.P; Teuber, J.P; Fernandez-Cuesta, I. Pillar-structured 3D inlets fabricated by dose-modulated e-beam lithography and nanoimprinting for DNA analysis in passive, clogging-free, nanofluidic devices. Nanotechnology 33, 2022, 385301, (12pp). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/ac780d.
2021
- Haugg, S.; Hedrich, C.; Blick, R. H.; Zierold, R. Subtractive Low-Temperature Preparation Route for Porous SiO2 Used for the Catalyst-Assisted Growth of ZnO Field Emitters. Nanomaterials 2021, 11 (12), 3357. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11123357.
2020
- Harberts, J.; Haferkamp, U.; Haugg, S.; Fendler, C.; Lam, D.; Zierold, R.; Pless, O.; Blick, R. H. Interfacing Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons with Designed Nanowire Arrays as a Future Platform for Medical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8 (9), 2434–2446. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0bm00182a.
2019
- Esmek, F. M.; Bayat, P.; Pérez-Willard, F.; Volkenandt, T.; Blick, R. H.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I. Sculpturing Wafer-Scale Nanofluidic Devices for DNA Single Molecule Analysis. Nanoscale 2019, 11 (28), 13620–13631. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr02979f.
- Harberts, J.; Zierold, R.; Fendler, C.; Koitmäe, A.; Bayat, P.; Fernandez-Cuesta, I.; Loers, G.; Diercks, B. P.; Fliegert, R.; Guse, A. H.; Ronning, C.; Otnes, G.; Borgström, M.; Blick, R. H. Culturing and Patch Clamping of Jurkat T Cells and Neurons on Al2O3 Coated Nanowire Arrays of Altered Morphology. RSC Adv. 2019, 9 (20), 11194–11201. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ra05320k.
- Hedrich, C.; Haugg, S.; Pacarizi, L.; Furlan, K. P.; Blick, R. H.; Zierold, R. Low-Temperature Vapor-Solid Growth of ZnO Nanowhiskers for Electron Field Emission. Coatings 2019, 9 (11), 698. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9110698.
- Fendler, C.; Denker, C.; Harberts, J.; Bayat, P.; Zierold, R.; Loers, G.; Münzenberg, M.; Blick, R. H. Microscaffolds by Direct Laser Writing for Neurite Guidance Leading to Tailor-Made Neuronal Networks. Adv. Biosyst. 2019, 3 (5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.201800329.
