ADAMOS
ADAMOS: Axion DAily MOdulation Searches
ADAMOS is a new fixed–frequency axion haloscope developed at the Universität Hamburg to explore dark matter axions around ≈ 20 GHz (∼ 83 μeV). The experiment employs an innovative thin-shell microwave cavity design installed inside the 14 Tesla superconducting warm-bore solenoid magnet available at the Institut für Experimentalphysik. This geometry maintains a large effective detection volume at high frequency, enabling sensitivity to a region of parameter space that is strongly motivated both by lattice QCD and axion quark nugget (AQN) phenomenology.
A central feature of ADAMOS is its continuously calibrated RF chain, which injects a pilot tone and performs periodic Y-factor measurements directly in situ to suppress temperature-dependent gain drifts of the amplifier chain. ADAMOS is designed to simultaneously support three complementary axion search channels without hardware reconfiguration: (1) cold dark matter axions via high-frequency (∼ 20 GHz) operation with heterodyne down-conversion to ∼ 10 MHz analysis band, (2) daily-modulated relativistic axions expected from AQN annihilation as the Earth rotates relative to the galactic wind, and (3) high resolution transient short-duration signals from streaming dark matter, potentially amplified by gravitational focusing in the solar system. A dedicated EMI/EMC veto channel, using an identical heterodyne chain, provides robust identification and rejection of environmental interference.
Commissioning is currently ongoing, with emphasis on cavity coupling optimisation, thermal and gain stability verification, and optimisation of the calibration cadence. Full scientific data taking is foreseen to begin early 2026. The platform establishes a high-frequency, high-stability axion search capability in Germany in an unexplored region of axion parameter space.
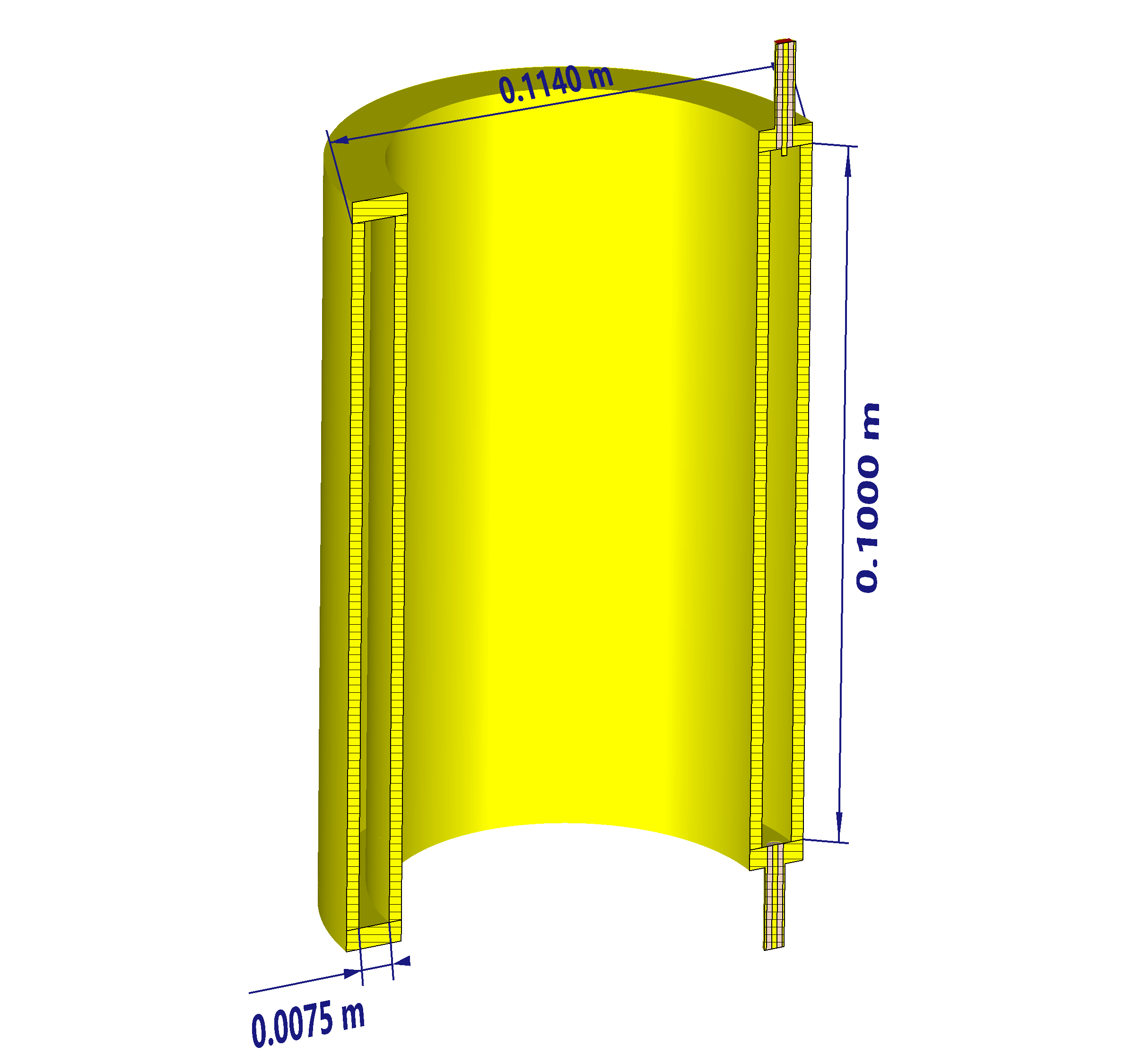
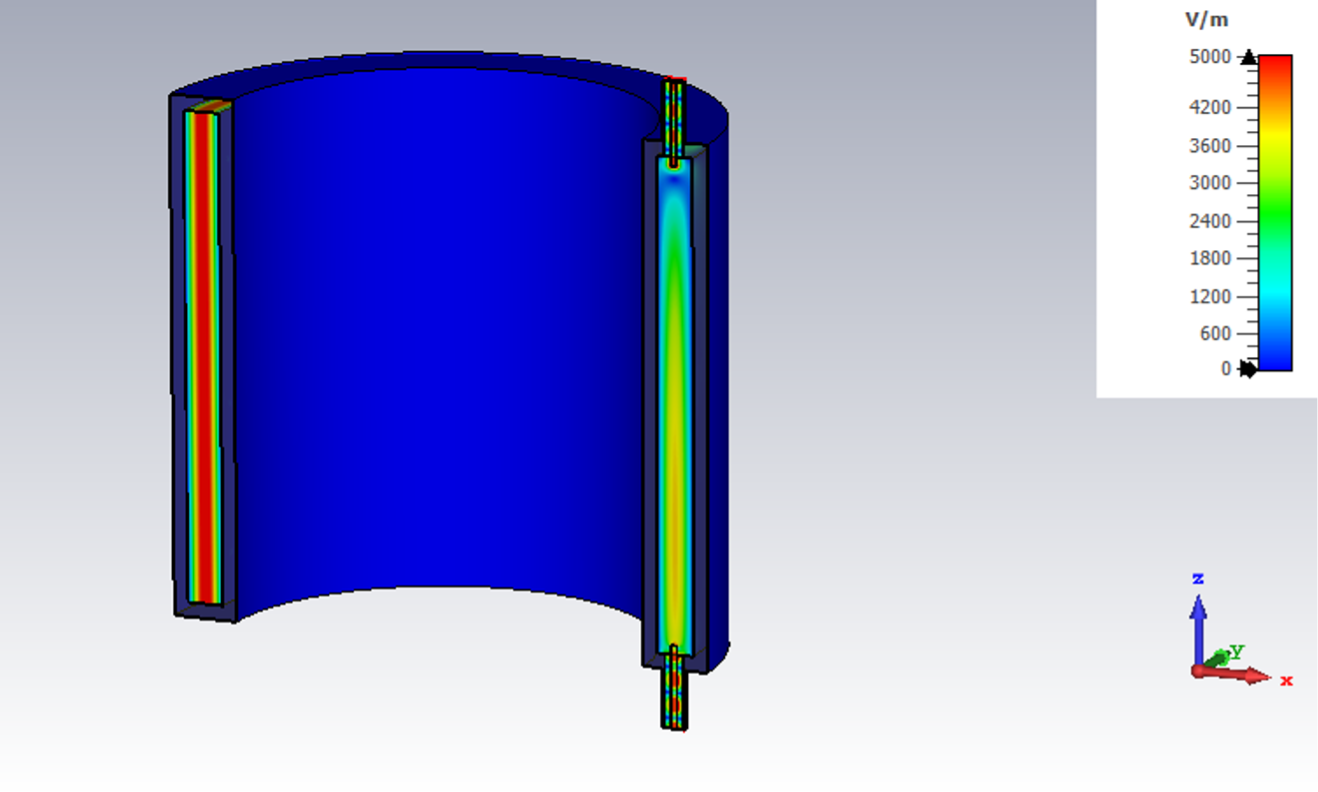
Figure 7: Top: CST model used for eigenmode and field simulations. Bottom: Preliminary mechanical design in FreeCAD. The thin–shell geometry uses two concentric cylinders with a 7.5 mm gap defining the TM010 mode volume.
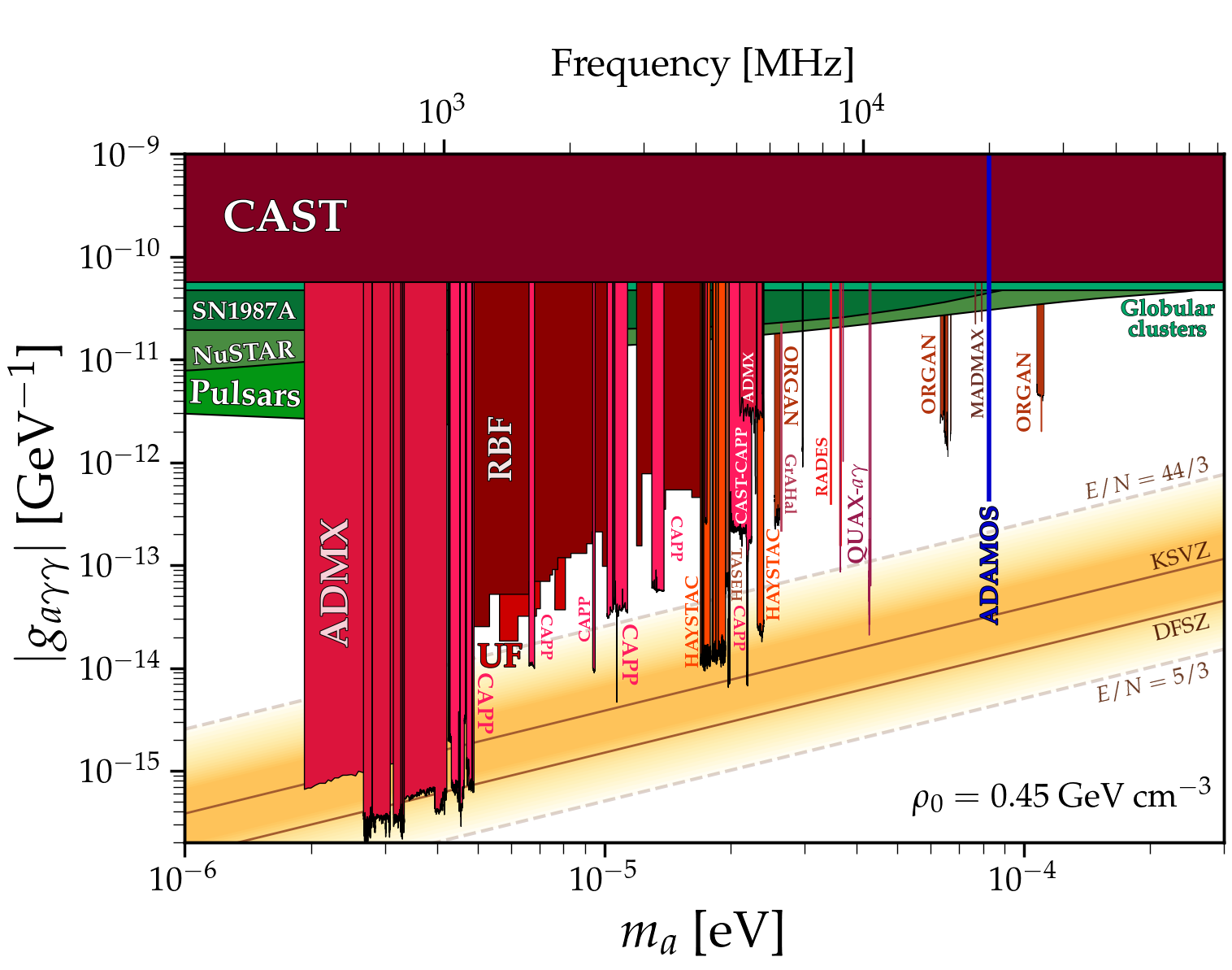
Figure 8: ADAMOS projected sensitivity (blue) for 30 days integration for CDM axions at 20 GHz compared to existing limits from other haloscopes (in red) and astrophysics (in green). The theoretical QCD axion band is also shown (in orange). Plot adapted from C. O’Hare, AxionLimits, Zenodo (2020), doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3932430.
Selected Presentations and Publications
- M. Maroudas, “Axion, ALP, and HFGW Searches Across Complementary Experimental Frontiers”, 20th Patras Workshop on Axions, WIMPs and WISPs, Lisbon, 24–26 Sept 2025. https://agenda.infn.it/event/46273/contributions/269303/
Interested in writing a thesis (BSc/MSc) on this topic? Take a look at our proposals.
